After installing iTunes on a Windows 7 guest, I would then plug my iPhone into a USB port on my CentOS 6 host. Inside of VMware Workstation 10, I selected the appropriate VM, then from the menu bar I selected VM > Removable Devices > Apple iPhone > Connect (Disconnect from host). This causes VMware to attach this USB device to the Windows guest instead of the CentOS host.
After doing this, I get the following message from VMware: “The Device “Apple iPhone” was not able to connect to its ideal host controller. An attempt will be made to connect this device to the best available host controller. This might result in undefined behavior for this device.”
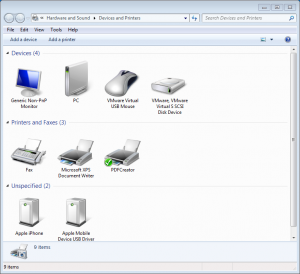
Go to Start > Devices and Printers. You should see two new devices under the Unspecified section called “Apple Mobile Device USB Driver” and “Apple iPhone”.
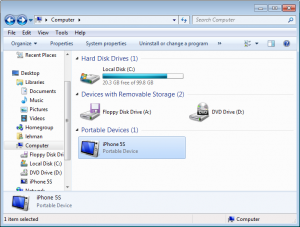
Also, if you open up Explorer and go to Computer, you should see your iPhone listed as a Portable Device.
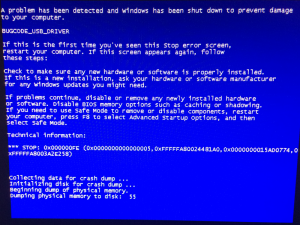
After browsing files on the iPhone within Explorer (using the iPhone as an internal storage device), I get a Windows blue screen including the message “BUGCODE_USB_DRIVER”. The guest machine crashes while the host remains stable.
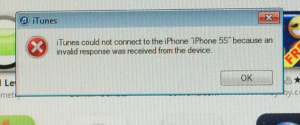
Alternatively, if I opened iTunes while the iPhone is attached to the Windows guest, iTunes would display the error “iTunes could not connect to the iPhone because an invalid response was received from the device.”
Ultimately, I resolved the majority of my issues by powering off the Windows guest VM, going to VM > Settings > USB Controller >
Change USB Compatibility from USB 1.1 to USB 2.0. Save and restart the VM.
Every once in a while iTunes does not recognize the iPhone. Usually this can be resolved, by removing and re-adding the iPhone or closing and re-opening iTunes. Sometimes by adding the iPhone prior to starting iTunes.
In order for Sync over Wi-Fi to work, the guest Windows VM running iTunes should to have an IP on the same physical network as your iPhone. Power off the guest VM, go to VM > Settings > Network Adapter >
Select “Bridged” instead of “NAT”.
My System Configuration
- VMware Workstation 10.1
- Host: CentOS 6.5 x86 64-bit
- Guest: Windows 7 Professional SP1
- iTunes 11.1.3.8
References
Installing VMware Tools on a Windows 7 Guest OS in VMware Workstation 10.1 running on a CentOS 6 host always resulted in the host OS crashing.
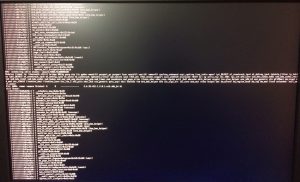
This appears to be due to a combination of VMware Workstation 10.1 running on CentOS 6 .5 with kernel 2.6.32-431.1.2.0.1.el6.x86_64 #1 SMP x86_64 GNU/Linux. I see these two interesting items on the screen output followed by a call trace.
BUG: scheduling while atomic: vmware/6035/0x000002000
Pid: 6035, comm: vmware Tainted: G D --------- 2.6.32-431.1.2.0.1.el6.x86_64 #1
To resolve this issue:
# service vmware-workstation-server stop
# service vmware stop
# mv -v /usr/lib/vmware/modules/binary /usr/lib/vmware/modules/binary~orig
# rm /lib/modules/$(uname -r)/misc/v*.ko
# depmod -a
# yum install make gcc keneral-headers-$(uname -r) kernel-devel
# /usr/bin/vmware-modconfig --console --install-all
# service vmware start
# service vmware-workstation-server start
I could now attempt to install VMware Tools on a Windows 7 Guest OS without the host crashing. However, I now ran into another complication. The VMware Tools install would hang around the point of installing the ThinPrint module. Basically, the VMware Tools install hangs due to cruft left over from previous install attempts. Follow VMware KB Article 1001354 to remove cruft left over from previous VMware Tools installs. Then try reinstalling again.
You do not need to repeat this procedure since the offending modules are being removed in the steps above. During subsequent kernel upgrades, modules will be recompiled automatically.
VMware claims that “this issue should be fixed with the next update (10.0.2), and we will publish a kb article.”
UPDATE: The VMware community appears to agree that this issue is resolved in the Workstation 10.0.2 release.
My System Configuration
- VMware Workstation 10.1
- Host: CentOS 6.5 x86 64-bit
- Guest: Windows 7 Professional SP1
References
By default, PuTTY does not retain very many lines of scrollback (output) in the terminal window. In order to increase this, go to:
- Category > Window > Control the scrollback in the window
- Increase the value for the “Lines of scrollback”
The largest allowable value is 1410065407.
After performing a base install of CentOS 6 using the minimal install CD, you may find that a lot of commands that you would expect are not there. Do the following to install additional, basic Linux packages that are common to most Linux distributions:
# yum groupinstall "Base"
Run the following in order to see detailed information including a description and which packages it will install.
# yum groupinfo "Base"
Group: Base
Description: The basic installation of CentOS Linux.
Mandatory Packages:
alsa-utils
at
authconfig
bc
bind-utils
centos-indexhtml
crontabs
cyrus-sasl-plain
dbus
ed
file
logrotate
lsof
man
ntsysv
parted
pciutils
psacct
quota
setserial
tmpwatch
traceroute
Default Packages:
abrt-addon-ccpp
abrt-addon-kerneloops
abrt-addon-python
abrt-cli
acpid
b43-fwcutter
biosdevname
blktrace
bridge-utils
bzip2
cpuspeed
cryptsetup-luks
dmraid
dosfstools
eject
ethtool
fprintd-pam
gnupg2
hunspell
hunspell-en
irqbalance
kexec-tools
ledmon
libaio
lvm2
man-pages
man-pages-overrides
mdadm
microcode_ctl
mlocate
mtr
nano
ntp
ntpdate
openssh-clients
pam_passwdqc
pcmciautils
pinfo
plymouth
pm-utils
prelink
rdate
readahead
rfkill
rng-tools
rsync
scl-utils
setuptool
smartmontools
sos
strace
sysstat
system-config-firewall-tui
system-config-network-tui
systemtap-runtime
tcpdump
tcsh
time
unzip
usbutils
vconfig
vim-enhanced
virt-what
wget
which
wireless-tools
words
xz
yum-plugin-security
yum-utils
zip
Optional Packages:
PyPAM
audispd-plugins
brltty
cpupowerutils
device-mapper-persistent-data
dos2unix
dumpet
ecryptfs-utils
edac-utils
genisoimage
gpm
kabi-yum-plugins
kernel-doc
linuxptp
logwatch
mkbootdisk
mtools
ncurses-term
nss_db
oddjob
pax
python-dmidecode
python-volume_key
rsyslog-gnutls
rsyslog-gssapi
rsyslog-relp
sgpio
sox
squashfs-tools
star
tboot
tunctl
udftools
unix2dos
uuidd
volume_key
wodim
x86info
yum-plugin-aliases
yum-plugin-changelog
yum-plugin-downloadonly
yum-plugin-tmprepo
yum-plugin-verify
yum-plugin-versionlock
yum-presto
zsh
There are additional package groups that may be useful in order to easily setup a particular service. To see a list of all the installed and available package groups:
# yum grouplist
My System Configuration
References
After performing a base install of CentOS 6 using the minimal install CD, do the following to install a basic GNOME desktop environment:
# yum groupinstall "Desktop" "Desktop Platform" "X Window System" "Fonts"
Run the following on a particular package group in order to see detailed information including a description and which packages it will install.
# yum groupinfo groupname
There are additional package groups if you want something more than a basic desktop environment. For example,
# yum -y groupinstall "General Purpose Desktop"
To see a list of all the installed and available package groups:
# yum grouplist
Once installed, you can start GNOME by running:
$ startx
or
$ /sbin/telinit 5
To have CentOS boot into runlevel 5 “X11” instead of runlevel 3 “Full multiuser mode”, modify the /etc/inittab file to change start up level from
id:3:initdefault:
to
id:5:initdefault:
My System Configuration
References
To expand the width of the main content page when using the WordPress 3.8 Twenty Fourteen theme:
- Login to WordPress as an administrator
- Go to Appearance > Widgets
- Remove all widgets from the Content Sidebar
- Go to Appearance > Editor > style.css
- Find the section that says:
.page-content {
margin: 0 auto;
max-width: 474px;
}
.page-content {
margin: 0 auto;
max-width: 990px;
}
My System Configuration
- WordPress 3.8
- Twenty Fourteen theme 1.0
References
David Lehman's System Administration Blog






